Orthopedic Solutions for Osteoarthritis: A Comprehensive Guide
February 9th, 2023 | 3 min. read
.png?width=674&height=449&name=Untitled%20design%20(72).png)
Osteoarthritis is a common condition affecting millions worldwide, causing joint pain and limiting mobility. If you or someone you know is living with osteoarthritis, it can be overwhelming to navigate the various treatment options and lifestyle changes that can help manage the condition.
This comprehensive guide will provide an overview of osteoarthritis, including causes, symptoms, and diagnostic tests. We’ll also delve into the different orthopedic solutions for managing osteoarthritis, including both non-surgical and surgical treatments and lifestyle changes that can make a big impact.
Introduction to Osteoarthritis
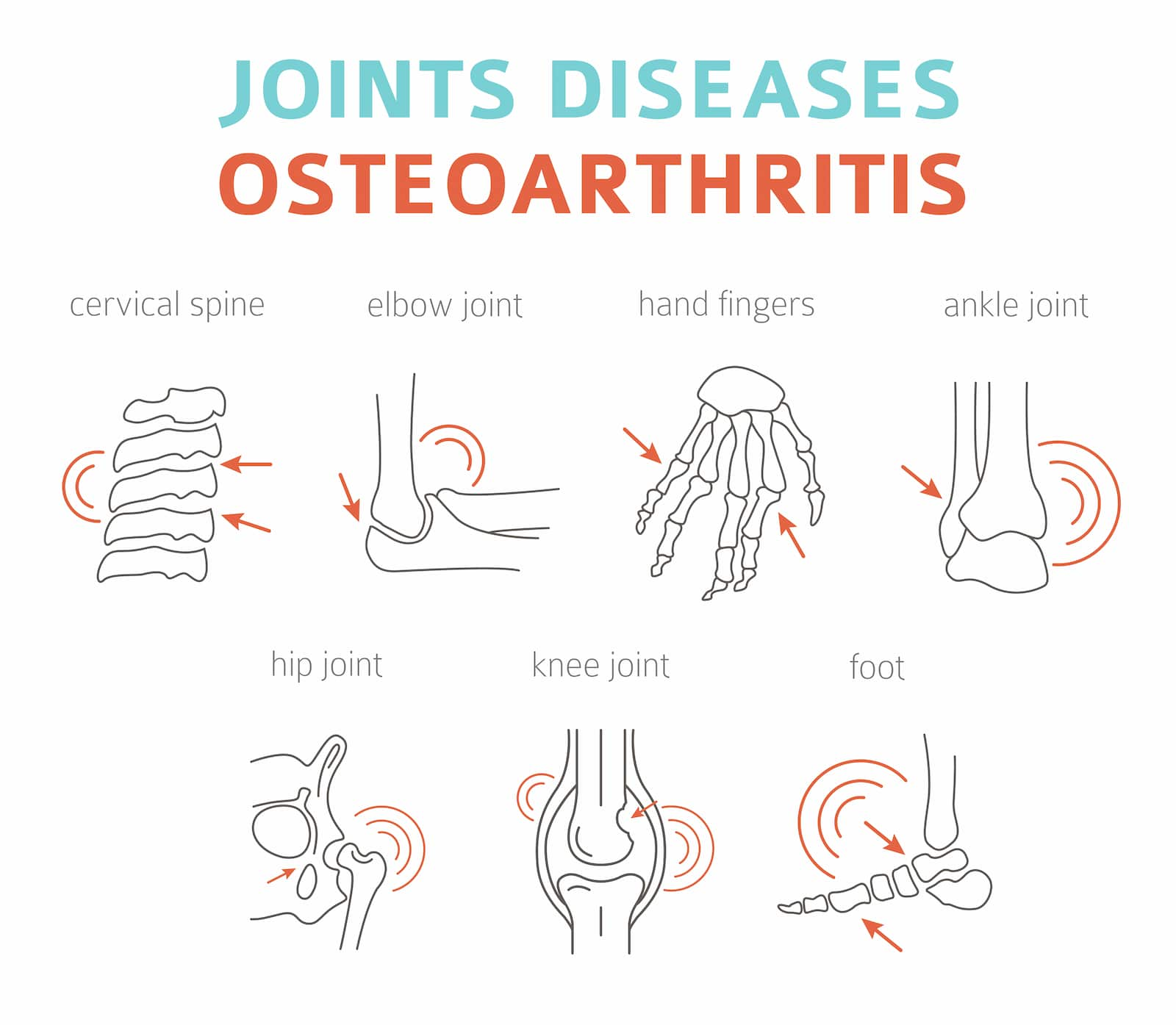
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects the cartilage in your joints, causing pain and inflammation. It is the most common type of arthritis, often called “wear and tear” arthritis. It can affect any joint but is most common in the hands, hips, knees, and spine.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 54 million adults in the United States have been diagnosed with osteoarthritis. This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, causing chronic pain, reducing mobility, and affecting daily activities.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide to orthopedic solutions for osteoarthritis. Whether you are seeking information for yourself or a loved one, this guide will provide the information you need to understand better the condition and the options available for managing it.
Interested in being evaluated for osteoarthritis in Corpus Christi, Texas?
Understanding Osteoarthritis
To effectively manage osteoarthritis, it’s important to clearly understand what causes the condition and what puts you at risk.
A. Causes of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints begins to wear down, causing the bones to rub against each other. This can cause pain, inflammation, and stiffness. The exact cause of osteoarthritis is not yet known, but risk factors include:
-
Age: Our joints naturally wear down as we age, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Genetics: Some people may be predisposed to osteoarthritis due to genetics.
-
Obesity: Excess weight puts extra pressure on joints, leading to osteoarthritis.
-
Joint injuries: Trauma or repetitive stress to a joint can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Overuse: Engaging in repetitive movements or overuse of a joint can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis.
B. Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis
In addition to the causes of osteoarthritis, certain factors can increase your risk of developing the condition. These include:
-
Age: As we get older, our risk of osteoarthritis increases.
-
Genetics: Some people may be more likely to develop osteoarthritis due to genetics.
-
Obesity: Excess weight can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Joint injuries: Trauma or repetitive stress to a joint can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Certain occupations: Jobs that involve repetitive stress or heavy lifting can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis
Diagnostic Tests for Osteoarthritis
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination and review your medical history to diagnose osteoarthritis. In addition, the following tests may be used:
-
X-rays: X-rays can help show the extent of joint damage and the degree of osteoarthritis.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides detailed images of your joints' soft tissues and bones.
-
Joint fluid analysis: A fluid sample from your affected joint may be taken to determine if there is inflammation or any other issues.
Orthopedic Solutions for Osteoarthritis
Several orthopedic solutions for managing osteoarthritis, including non-surgical and surgical treatments.
A. Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments can help relieve pain, improve mobility, and slow the progression of osteoarthritis. These treatments include:
-
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint function and decrease pain through exercise and stretching.
-
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the stress on your joints and relieve symptoms of osteoarthritis.
-
Assistive devices: Canes, walkers, or knee braces can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
-
Hot and cold therapy: Using hot and cold therapy can help relieve pain and swelling.
B. Surgical Treatments
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat osteoarthritis. These procedures may include:
-
Joint replacement: Joint replacement surgery involves removing and replacing the damaged joint with an artificial joint.
-
Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves making small incisions in the affected joint to repair or remove damaged tissue.
-
Osteotomy: Osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and reshaping a bone to relieve pressure on the affected joint.
Working with a healthcare provider is important to determine the best course of action for your specific needs and medical history.
Lifestyle Changes for Osteoarthritis
In addition to medical treatments, you can make several lifestyle changes to help manage osteoarthritis symptoms and improve your quality of life. These include:
-
Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve joint function and relieve pain. Low-impact activities such as swimming, cycling, and yoga are recommended.
-
Diet: Eating a healthy and balanced diet can help manage weight, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health.
-
Stress management: Chronic stress can increase osteoarthritis risk and worsen symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques such as meditation or deep breathing into your daily routine can help.
-
Sleep: Sleeping is important for overall health and can help reduce pain and inflammation.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a common condition affecting millions worldwide. With the right combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes, it’s possible to manage the symptoms of osteoarthritis and improve your quality of life. If you or someone you know is living with osteoarthritis, we hope this comprehensive guide has provided valuable information and insights into the various orthopedic solutions available.
Dr. Williams has been practicing orthopedic surgery in Corpus Christi since 1998. After graduating from Texas Tech hereceived his medical degree from the University of Texas at San Antonio. At the prestigious Campbell Clinic located at the University of Tennessee, Dr. Williams completed not only an Orthopedic Surgery Residency, but an additional year of Fellowship Training in Spine Surgery. Dr. Williams is dedicated to creating an excellent patient experience in the office or in the surgery suite.
Topics:

