Common High School Basketball Injuries: Signs, Symptoms and Treatments
January 27th, 2017 | 7 min. read
High school basketball comes with its share of injuries. Basketball is an aggressive, fast-moving sport. In spite of the foul rules, players still collide, land on each other’s feet, elbow and shove, and trip and fall on their way to the ball. It’s all part of the game of getting possession and making one’s way down the court.
Collisions and contact aren’t the only causes for injury. Intense sprints, starts and stops, lunges, reaches, and pivots can all lead to muscle, tendon, or ligament strains. Handling the ball can lead to jammed fingers. Landing after layups and jump shots can also be hard on the knees and ankles.
High school basketball doesn’t have to be hard on a young player’s body, however. If you know the most common injuries, you can prepare yourself with conditioning and equipment. Smart play can also help to minimize accidents on the court.
COMMON High School BASKETBALL INJURIES
Muscle Strains
Pulled muscles are some of the most common injuries in any high school sport. These soft-tissue injuries are most likely to occur when you stretch your muscle past its normal limit. They’re even more common when muscles are worked out “cold,” meaning they haven’t been sufficiently warmed up before play or stretched after and between workouts.
What is a muscle strain, exactly? The fibers of the muscle tear, leading to a burning pain that can be temporarily disabling. A strain, particularly in the leg muscles, may take a player out of the game and possibly out of the season, depending on its severity.
In basketball, a muscle strain can happen any variety of ways. For example, you might:
- Overstretch a back muscle when you pivot and dodge to keep the ball away from an opponent.
- Pull a thigh muscle when sprinting or lunging.
- Strain a calf muscle when springing upward to make a jump shot.
Strains can also happen when a muscle is subjected to a load (weight, pressure, or force) it doesn’t have the power to counteract.
In basketball, this could happen during a bad fall against a hard floor. It could also happen if you’re pushed or shoved by an opponent and you try to push back using a muscle that isn’t strong enough for the task at hand.
Muscle Strain Symptoms
You may experience one or more of the following:
- A popping sound
- Sharp or burning pain
- Tenderness when you touch the muscle
- Swelling
- Bruising
Treatment of Strains
In most cases, muscle strains can be treated immediately with RICE therapy. Take yourself out of the game and let a coach know you need to ice your injury. You can also take NSAIDs (like ibuprofen or acetaminophen) to reduce inflammation and pain. Rest your muscle for a few days to a few weeks until the pain subsides.
In severe cases, a muscle strain may require several weeks of rest, immobilization (for example, using a bandage wrap or splint), and physical therapy rehab. In the case of a complete muscle tear or rupture, surgery may be needed to repair the tissue.
Finger Injuries

Fingers frequently get hurt in the context of playing basketball. For example:
- Gripping the ball can lead to overuse injuries like tendonitis.
- When intercepting passes, being blocked/fouled, or struggling to keep possession of a ball, players may also jam or stub their fingers or bend them back too far, leading to ligament sprains and or muscle strains.
- Falls or collisions can happen with enough force to cause fractures or cuts.
Finger Injury Symptoms
- Pain
- Popping or cracking sound
- Inability to move the affected finger
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Visible deformity (the finger is suddenly crooked, for example)
Treatment of Finger Injuries
If you’ve injured your finger or have the above symptoms, take yourself out of the game and tell a coach. In the case of a fairly minor injury, first-aid may involve bandages, RICE therapy, and/or taping two fingers together to immobilize and stabilize the injury.
See a doctor as soon as you can to diagnose the injury and prevent further damage or future problems using your finger or hand.
Knee Injuries: Patellar Tendonitis and ACL Tears

Patellar Tendonitis
This is an overuse injury common to basketball players. The patellar tendon is the fibrous band that runs along the front center of the knee, connecting the kneecap (patella) to the shin. This tendon works in tandem with the thigh muscle (quadriceps) to bend and straighten the knee.
When you overuse this function of the knee by repeatedly jumping, landing, and squatting (as you do before making a shot), the tendon can develop small tears that multiply too fast for the body to repair. As a result, the tendon becomes inflamed and the knee can become sore and stiff.
Patellar Tendonitis Symptoms
- A sore, dull pain along the front of the kneecap
- Pain during and after activity (especially when jumping)
- Pain when bending the knee or kneeling
Treatment for Patellar Tendonitis
- Rest
- Ice therapy for inflammation
- NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
- Wearing a knee brace to compress and stabilize the knee
- Stretching the leg muscles (calves, quads, and hamstring)
ACL Tears
The ACL, or anterior cruciate ligament, is one of the four major ligaments of the knee joint. Together these four ligaments hold the upper and lower legs together and provide stability to the knee.
The ACL, a braid-like cord made of strands of collagen, is in the center of the knee and controls forward movement of the shin bone as well as rotation. You use the ACL whenever you step forward or kick.
When the ACL is strained and sustains a tear, the entire knee can become unstable. Though the severity of tears range from very mild to severe, most players who injure their ACLs know it at the time. If you’ve torn your ACL, you will most likely find you’re unable to turn, twist your leg, or pivot.
Basketball players are particularly susceptible to ACL damage because of the sudden, abrupt movements they make: sudden decelerations (slow-downs and stops), cutting motions to the side (when dodging to get around another player), and landings after making jump shots and layups.
ACL Tear Symptoms
- A loud “pop” or snapping sound
- A buckling or giving way of the knee
- Inability to put weight on the knee
- The knee sliding out of the joint
- Pain, especially when moving
- Swelling
Women and girls are more prone to ACL tears than men. For this reason, many orthopedists and sports medicine centers run specialized ACL awareness clinics for female athletes. In these clinics, athletes learn exercises, safety tips, and other techniques to help minimize their risk of injury.
ACL Tear Treatment
- RICE therapy as a first-aid treatment
- NSAIDs for pain and swelling
- See a physician or orthopedist as soon as you can to diagnose your injury and to discuss non-surgical and surgical treatment options
ACL injuries do not always require surgical repair, but they should be seen. Living with an untreated ACL tear can compromise your knee’s stability or lead to future injury or osteoarthritis.
If you are interested in learning about our knee conditioning program click here!
Ankle Injuries: Ankle Sprains and Achilles Tendonitis
With all the sudden pivots, shifts, turns, and jumps involved in basketball, ankles are are particularly vulnerable to injury.
Ankle sprains

An ankle sprain, also known as “rolling” an ankle, occurs when the foot rolls inward or outward, overstretching the ligaments on the inside or outside of the foot.
In the majority of cases, ankles tend to roll outward, tearing the ligaments that run along the outer edge of the foot.
This can happen in a game when you land awkwardly on a jump shot — most commonly, if you come down on another player’s foot. The contact with the uneven surface can make your landing unstable, causing the ankle to roll.
Sprained Ankle Symptoms
- Pain
- Popping sound
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Warmth over the injury area
- Tenderness when you touch the ankle
Some people can put weight on their sprained ankles; others may find it too painful, and could require help getting off the court.
Sprained Ankle Treatment
RICE therapy is the first course of action if you’ve sustained a sprain. Bringing the swelling down is your main goal, along with managing pain and resting the affected ankle. You can continue this treatment for up to 48 hours.
See a doctor or orthopedist to rule out more serious injuries like full ruptures, fractures, or damage to surrounding tissue. You may also need rehab with a sports medicine professional.
Achilles Tendonitis
Tendonitis has two acceptable spellings: “tendonitis” and “tendinitis.” Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury common in many sports, and especially common in runners and basketball players. It’s an inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the fibrous cord that attaches your calf muscle to your heel. It’s purpose is to raise your heel off the ground and to lower it back down — movements you use when standing on tiptoe, jumping, landing, walking, and running.
Basketball players use all these heel-raising motions regularly, which makes them particularly susceptible to this injury. Players with tight, poorly stretched calf muscles are particularly vulnerable.
Achilles Tendonitis Symptoms
- Pain — dull or sharp — at the back of the ankle or lower part of the calf; this pain may increase during or immediately after activity
- Swelling
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment
- NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
- Ice therapy and rest to help to reduce swelling and discomfort
- Wrapping or taping with kinesio tape
- Orthotics (custom shoe inserts that raise the heel) to minimize the stretching of the tendon when walking
- Physical therapy, including stretching and strengthening calf muscles
Shin Splints
Shin splints are stress injuries — inflammation of the bone tissue, tendons, and muscle of your shinbone (tibia). Usually you’ll 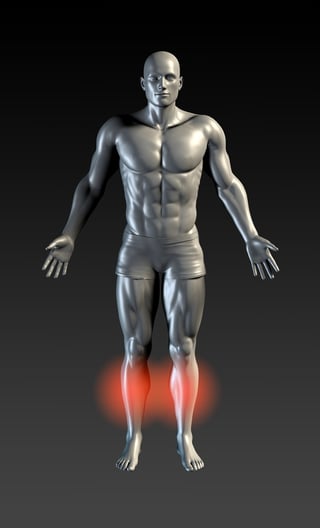 feel the soreness and tenderness along the inside of the front of your leg.
feel the soreness and tenderness along the inside of the front of your leg.
Shin splints are caused by the force impact of running on a hard surface. They can happen in any sport, though they’re most commonly seen in athletes who are new at running on roads. Athletes who suddenly increase their exercise frequency or difficulty may also notice this pain.
Shin Splints Symptoms
- Pain, either sharp or throbbing, along the inside front of the shin
- Pain that increases during and immediately after activity
- Tenderness and soreness that responds to touch
Shin Splints Treatment
- RICE therapy for pain
- NSAIDs for pain and inflammation
- Supportive footwear with arch support and thick soles, to help correct flat feet and to provide cushioning when running or jumping
- Orthotics to help support low arches
Shin splints, though painful, are minor and extremely common. They’re seen more often in people with low or rigid arches or flat feet. Athletes who are using worn out or thin-soled shoes may also be at risk. Overtraining can also lead to splints.
WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR
For minor basketball injuries like bruises and muscle strains, you can usually self-treat at home with ice therapy and NSAIDs to help with pain and swelling. The important thing is to get rest and not overtrain when you know you’re injured.
However, when in doubt, see a physician or orthopedist. Sometimes, injuries that seem minor may actually require physical therapy, sports medicine, or orthotics. Left untreated, some orthopedic injuries can lead to alterations in the way you walk, run, throw, or perform other activities.
These little shifts in the short run may affect your healing and the quality of your game. In the long run, they can lead to more serious problems like osteoarthritis or tendon ruptures.
Also, if you sustain a head injury after a collision or fall, always visit a doctor as soon as you can. You may have a concussion, which is a mild traumatic brain injury.
Article written by: Rob Williams, MD
Call Coastal Orthopedics located in Corpus Christi, Texas at 361.994.1166 today!
Dr. Williams has been practicing orthopedic surgery in Corpus Christi since 1998. After graduating from Texas Tech hereceived his medical degree from the University of Texas at San Antonio. At the prestigious Campbell Clinic located at the University of Tennessee, Dr. Williams completed not only an Orthopedic Surgery Residency, but an additional year of Fellowship Training in Spine Surgery. Dr. Williams is dedicated to creating an excellent patient experience in the office or in the surgery suite.
Topics:

