When do I need a Total Knee Replacement? (Signs and Symptoms)
April 11th, 2016 | 3 min. read
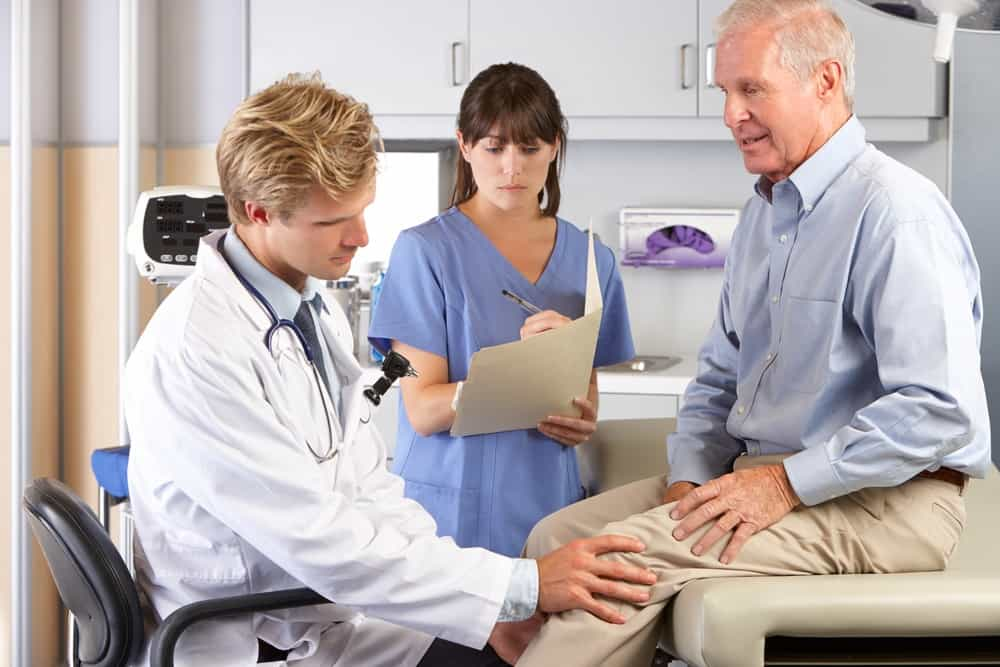


If your knee joint is severely injured or damaged by a disease like arthritis, a total knee replacement (also called knee arthroplasty) may be the answer for you. But how do you know if you're a candidate and if the time is right?
Because total knee replacement is a major surgery, orthopedists prefer to begin with non-invasive treatment options. For that reason, most patients who undergo knee arthroplasty are at "the end of the line" with non-invasive approaches. They've tried everything to improve mobility and reduce pain, but nothing has worked for long.
If you've tried a variety of treatments for your knee pain and you're not seeing results, it may be time to visit an orthopedist to talk about a total knee replacement.
do i need a new knee? signs and symptoms
Contrary to what many people may believe, age is not necessarily a major factor in knee arthroplasty. Juvenile arthritis can cause pain and disability to the point where a knee replacement may be recommended in children and teens.
However, most patients are adults between the ages of 50 and 80 who suffer from degenerative arthritis (osteoarthritis), a breakdown the cartilage cushion between the bones of the knee joint. In most cases, this type of arthritis is age-related.
Are you unsure about whether your knee is really that bad? Check your knee symptoms against the following list. Are you experiencing:
- morning joint stiffness lasting less than 30 minutes?

- chronic swelling or inflammation that doesn't respond to rest or medication?
- severe to moderate pain that interferes with your daily activities?
- deformity of the knee, such as a bowing in or out?
- aching or pain after extensive standing, walking, or exercise?
- pain that increases during humid or rainy weather?
- pain that interferes with your sleep?
- pain while resting: persistent or intermittent aching without a particular cause?
- swelling or stiffness, especially after periods of rest or inactivity?
- loss of mobility (trouble bending and straightening the knee)?
- a grating or grinding feeling in the joint?
- difficulty climbing stairs or getting in and out of chairs or tubs?
- no relief from pain, even when using a cane or walker?
- no relief from treatments like sports medicine/physical therapy, aquatic therapy, cortisone or lubricating injections, medication, or other, less invasive surgeries?
If you suffer from any of the above, you may be a candidate for a total knee replacement. The next step is to visit an orthopedic surgeon to be diagnosed and evaluated.
getting diagnosed
An orthopedic surgeon can diagnose your knee condition with a thorough examination. You'll be asked to describe your medical history, your pain, your current level of function, and any known injuries that may be contributing to your knee problems.
Your doctor will perform physical tests to check your knee for range of motion, alignment, and strength — for example, you may be asked to walk and to bend your knee. X-rays or MRIs may be required to determine the extent of any bone damage, tissue damage, or irregularities in your knee. (If you have significant bone loss and weakness or an infection, you may not be a good candidate for the surgery.)
At the end of your visit, your orthopedist will present you with treatment options and discuss with you whether knee replacement surgery is an advisable option for improving your pain and ability to function.
What is a total KNEE replacement, exactly?
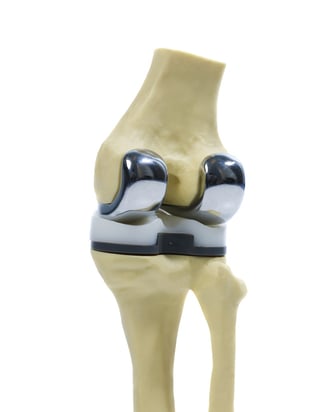 In a knee arthroplasty, your orthopedic surgeon will not give you an entirely new joint.
In a knee arthroplasty, your orthopedic surgeon will not give you an entirely new joint.
Rather, the surgeon repairs your existing bone by removing damaged or diseased parts.
Your bones are then resurfaced with contoured metal or plastic implants.
The surgeon presses or cements the new components in place, using spacers to ensure that your bones will glide smoothly over each other — just like your "real" knee before it became damaged.
KNEE ARTHROPLASTY: OUTLOOK
Knee arthroplasty is a safe and effective procedure that is performed on over 600,000 people per year in the U.S. Reported complication rates are very low.
However, all surgeries have risks. Infection, blood clots, scarring, and injuries to the blood vessels and nerves around the knee are all rare but possible complications from surgery.
Continued pain is also possible. However, most patients and surgeons report great satisfaction with knee replacement surgeries, with over 90% of patients reporting an improvement in their pain and function.
Knee implants can wear out, however. Your orthopedic surgeon may suggest that in the future, you refrain from high-impact sports like running or basketball, as these will speed up the wear-and-tear on your implants.
For the best results, try low-impact activities instead. Sports like swimming, walking, kayaking, golf, and biking are kinder on your joints and will help your "new knee" perform well for many years.
SHOULD YOU CONSIDER a knee replacement?
The answer depends on many factors, including your age, health history, lifestyle, and medications you may be taking. Give Coastal Orthopedics located in Corpus Christi a call 361.994.1166 to find out if arthroplasty may be the right choice for treating your knee pain.
Dr. Williams has been practicing orthopedic surgery in Corpus Christi since 1998. After graduating from Texas Tech hereceived his medical degree from the University of Texas at San Antonio. At the prestigious Campbell Clinic located at the University of Tennessee, Dr. Williams completed not only an Orthopedic Surgery Residency, but an additional year of Fellowship Training in Spine Surgery. Dr. Williams is dedicated to creating an excellent patient experience in the office or in the surgery suite.
Topics:


